Motivation
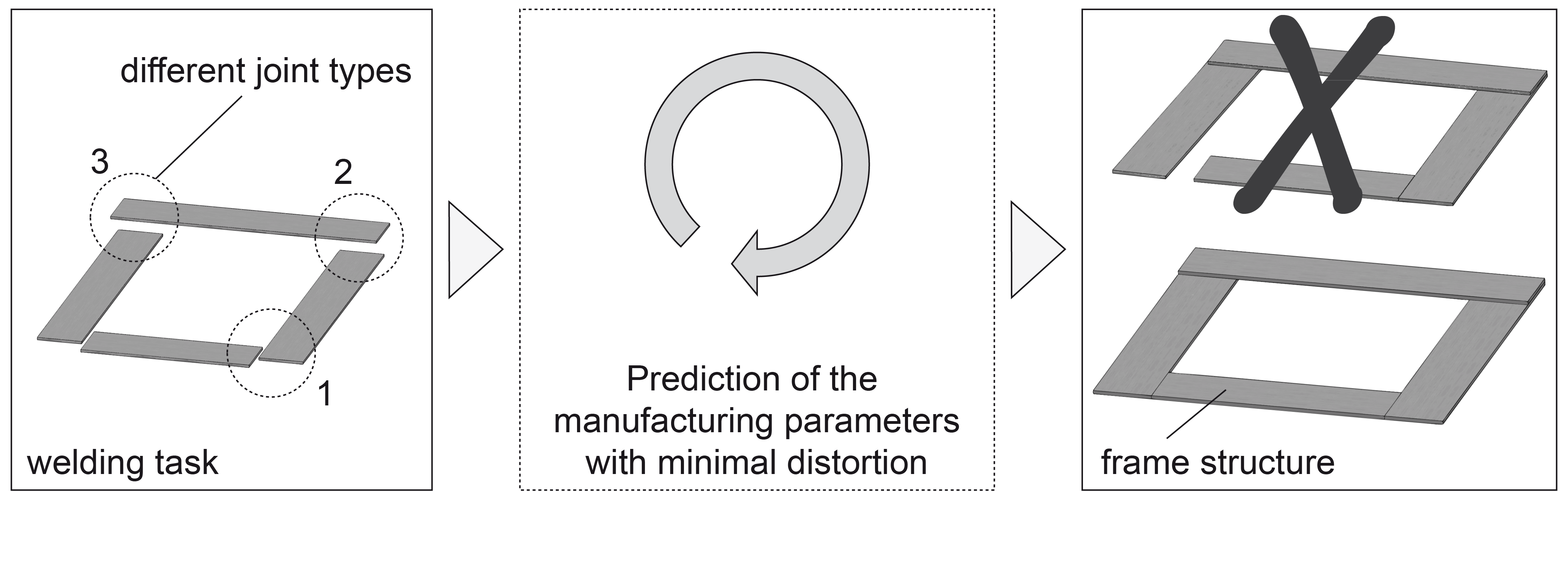
Laser beam welding is a fast and flexible joining process. Although laser-welded components experience minimal energy input along the weld line, component distortion still occurs, and this can lead to parts that do not meet the dimensional tolerance requirements. Therefore, additional processing steps such as thermal or mechanical straightening are required. Simulation-based investigations within numerous research works have contributed to a better understanding of distortions and to a more accurate prediction of component distortions for simple geometries. However, for complex geometries, the numerical determination of appropriate process parameters for minimal component distortion leads to rising costs due to increased computational expenses. Moreover, the construction of the numerical model contains many manual processing steps and requires a high degree of user expertise. The size of these complex geometry models therefore requires a new approach for the distortion computation and minimization within a reasonable time.
Objective
The aim of the project is to develop and validate a more efficient numerical method to predict the appropriate process parameters for laser beam welded parts with complex geometries while minimizing component distortion. An additional goal of this project is to demonstrate a possible way to couple and automate the single modelling steps and to make the user control more user-friendly.
Approach
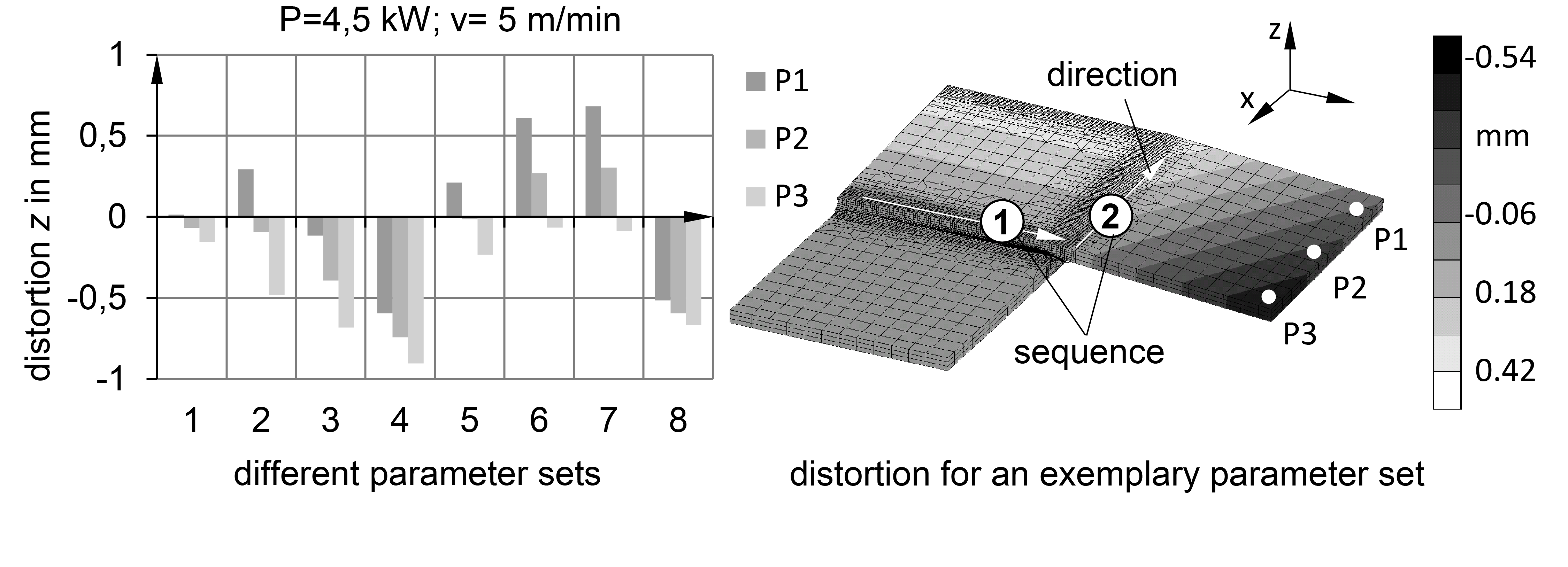
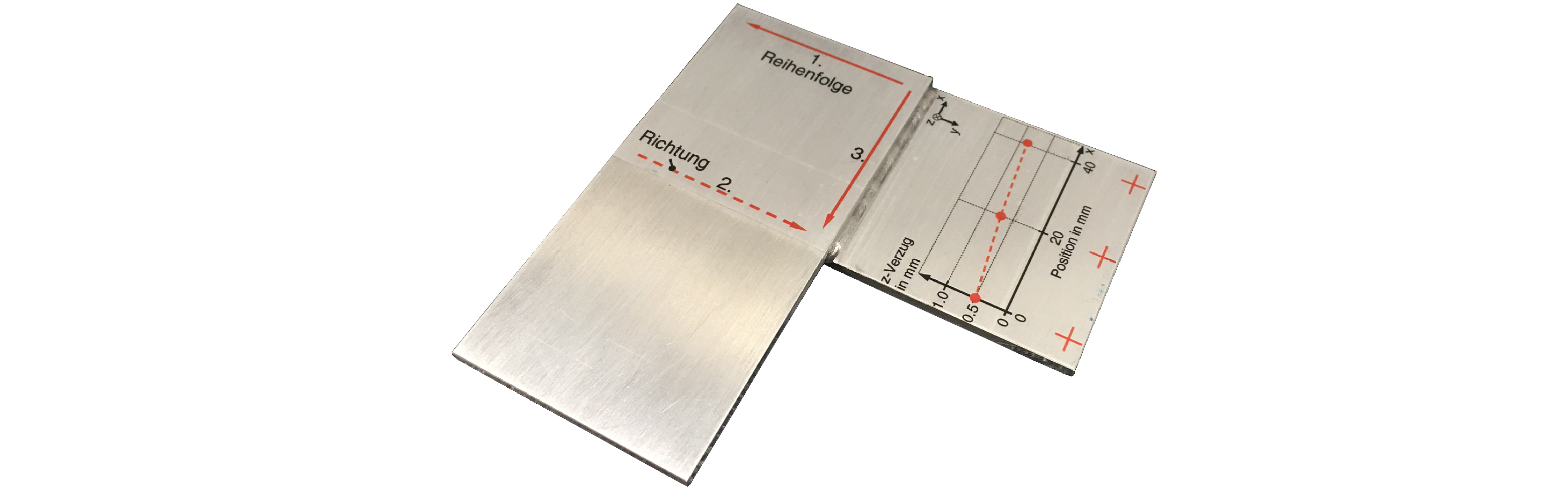
In order to predict the appropriate process parameters based on numerical methods, a complex geometry has to be divided into subareas – similar to the so-called local-global-method, but with different joining operations. Subsequently, with regard to the residual stresses and the component distortion, these subareas have to be numerically analyzed. The computed distortions of the subareas can then be employed to compute the distortion of the whole complex geometry. The application of this method in combination with the use of artificial intelligence (AI) will facilitate the prediction of appropriate process parameters for minimal component distortion in welded geometries.
Results
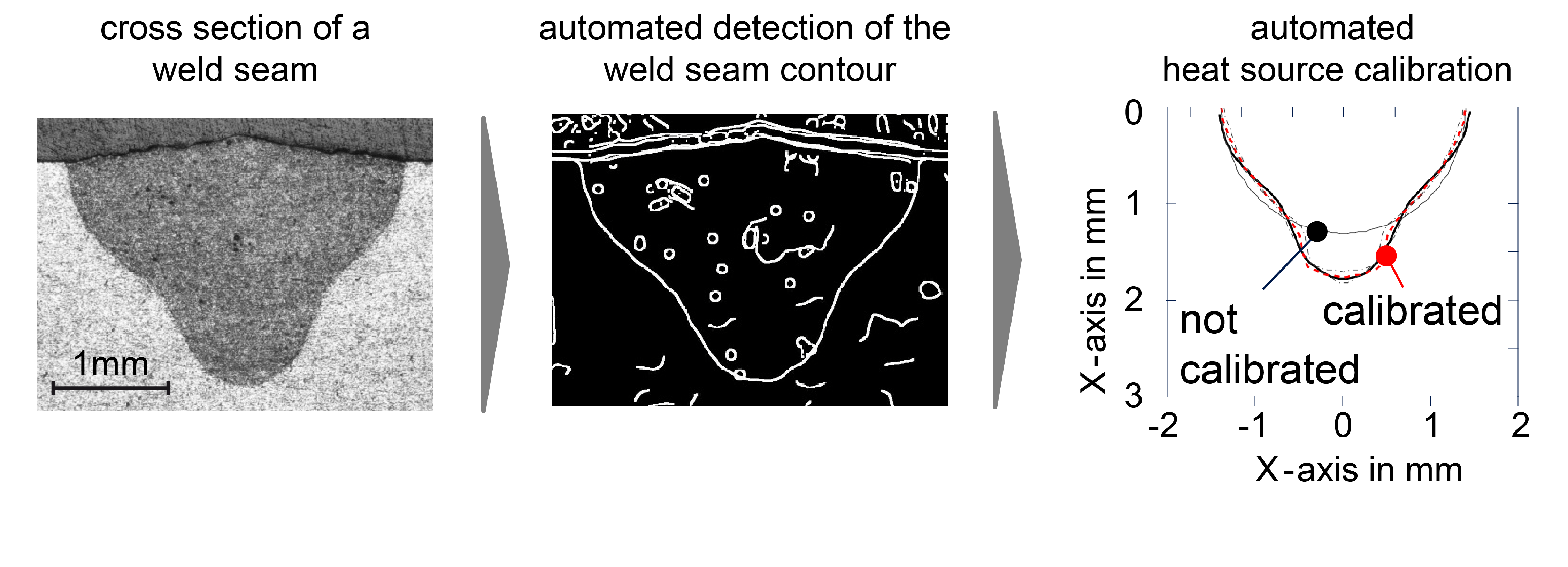
Based on the former work at the iwb pertaining to the calibration of temperature fields, a novel approach for the automated heat source calibration was developed. Moreover, using a simplified geometry with two weld seams as an example, the potential to minimize the component distortions with genetic algorithms (GA) was shown. In addition to the minimization of component distortions, a method for the efficient application of previously-calculated component distortion was implemented.
Acknowledgement
This research and development is based on investigations from the project ReVeBa – Computerized Distortion Minimization of Laser Beam Welded Complex Components, which is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG).