Research Topic
| Short Title | Local Gear Power Loss |
| Start of Project | Q1/2023 |
| Funding | FVA-Nr. 686/II Research Association for Drive Technology e.V., FVA |
| Contact | Dr.-Ing. T. Lohner |
Project Description
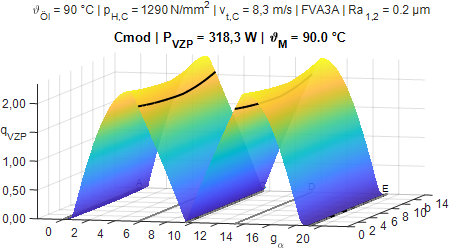
Over wide operating and application ranges, the load-dependent gear power loss accounts for a significant proportion of the total power loss of a gear unit and is thus decisive for its efficiency behavior. The most accurate possible calculation of the load-dependent gear power loss is therefore highly relevant for an accurate computational mapping of the efficiency and thermal balance of gearboxes.
The gear power loss is usually calculated from the product of the input power PA, a mean gear friction coefficient μmz and a (local-) geometric tooth loss factor HV(L). The calculation approaches established in practice for determining the mean coefficient of friction are usually based on measured loss torques of unmodified spur test gears. These calculation approaches refer to operating parameters at the pitch point. Hence, the meshing conditions on which the test gears are based on are implicitly taken into account. Since practical gears usually differ significantly from test gears, this leads to an error in the calculated gear friction.
The research objective is to increase the calculation quality and depth of efficiency and heat balance by the local calculation of the gear power loss (cf. Fig. 1). A validated, practicable calculation method for determining the local gear power loss of practical gears of any geometry is developed. For this purpose, a method carrier is built up and validated with, among other things, models for determining lubricant film thickness parameters and rheological fluid models for calculating the local coefficient of friction. Subsequently, established, averaged calculation approaches will be classified for application to practical gears, and a detailed analysis and classification of all the calculation approaches used will support the user in the selection of a suitable calculation approach in the future.