Pick-by-Light picking system based on passive RFID tags
In manual order picking systems, pick-by-light systems are often used to support order pickers and increase performance. By displaying the picking compartment and the picking quantity, a high picking performance with low error rates can be achieved. The weak points of such systems are the high costs and the low flexibility due to the wire-bound assembly at each storage compartment. The aim of the Pick-by-Tag project is to develop a new order picking system based on displays without power supply that are activated via RFID tags.
Pick-by-Light (PbL) is a widely used system for manual picking. The basic elements are LEDs to visually assist order pickers in finding the picking compartment, a display to indicate the picking quantity and a button to confirm the picking or to make corrections. PbL systems can generally be divided into wired and wireless systems, the first being used much more frequently.
The wired version is connected to a central control system via cables or wires. However, the advantage of a permanent power supply is opposed by negative aspects such as high installation costs, low flexibility with regard to installation and stock restructuring and high investments.
Existing wireless PbL systems are controlled centrally via remote control. Radio transmission increases flexibility and simplifies installation, but battery operation significantly increases maintenance requirements. In this case, it is usually necessary to change the batteries every three to twelve months. This is why wireless PbL displays have rarely been used so far, and mainly in smaller warehouses.
The objective of the research project is to develop a pick-by-light picking system based on passive RFID tags that do not require an individual power supply.
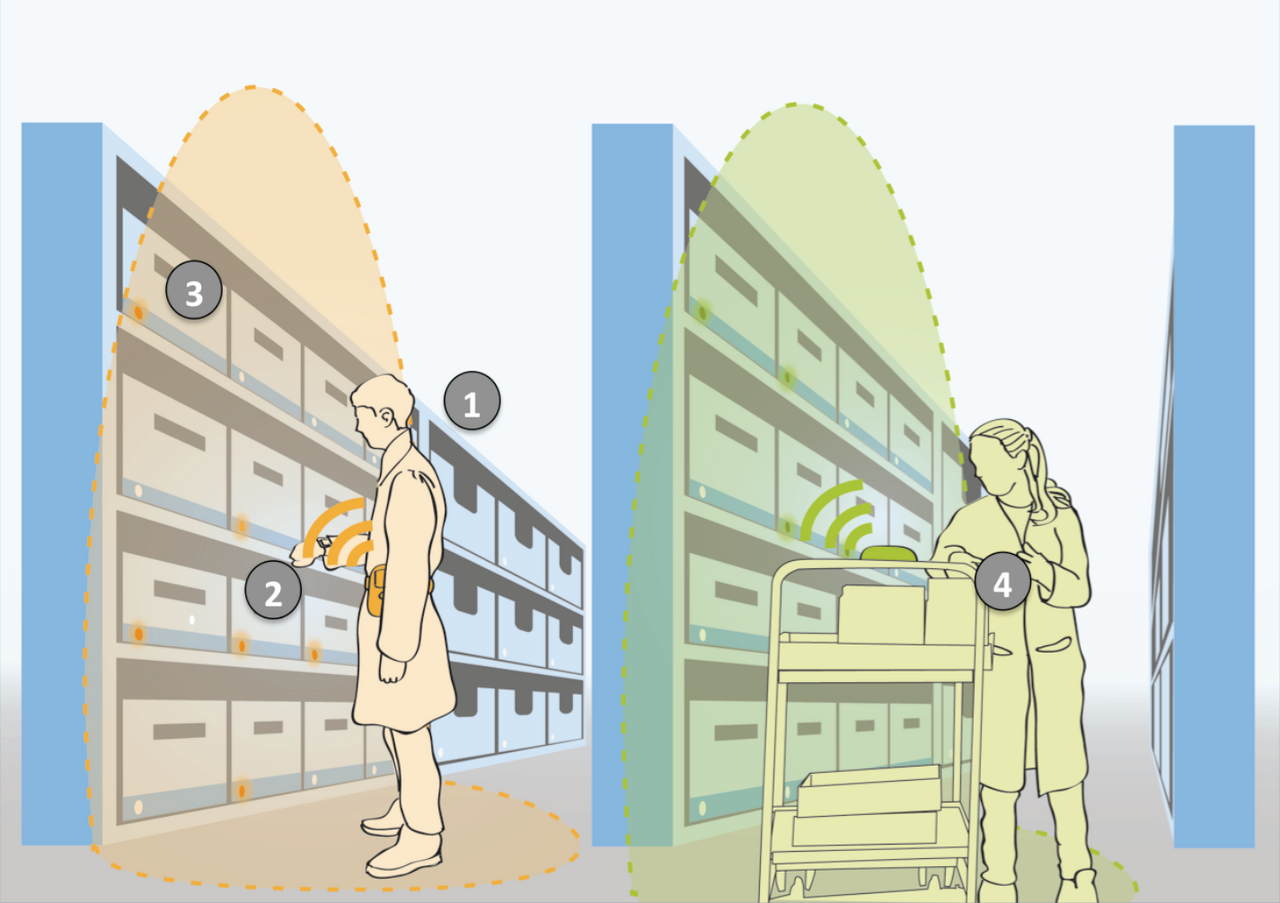
In this way, the advantages of the Pick-by-Light technology can be used and its disadvantages are avoided. The Pick-by-Tag system must be designed in such a way that the compartment displays can be placed anywhere. The wireless functionality should also significantly reduce the costs for acquisition, installation and maintenance. The shelf displays, which are based on passive RFID tags, are activated using a wireless signal from an RFID reader. Additional information such as the withdrawal quantity may be displayed to the order picker on a display. As shown in Figure 1, a mobile data terminal (MDT) (1) or an installation on a picking cart (4), for example, can be used. These send out an RFID signal (2) that activates all order-relevant shelf displays (3).
The low installation costs and acquisition costs are intended to make the pick-by-tag system also interesting for SMEs for whom conventional systems are too expensive.
The first step in the project is to evaluate existing PbL systems and their areas of application at project partners. The findings are used to derive requirements for the new system, which - supplemented by further requirements from standards and directives - are then documented in a catalogue of requirements.
Technical and logistical concepts for the pick-by-tag system will be developed on this basis. On the hardware side, component tests are initially planned to ensure that the RFID modules have a suitable structure. The software for controlling the RFID tags and the connection to a warehouse management system is then programmed.
The technical components are first tested under laboratory conditions to determine any further requirements. The final evaluation of the overall system is carried out by field tests with several industrial application partners. Here not only objectively measurable (e.g. error rate) but also subjective criteria (e.g. acceptance of the system) are included in the evaluation.
The project is carried out in cooperation with the Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits (IIS).
- CIM GmbH
- Elabo GmbH
- FIS GmbH
- Gebhardt Fördertechnik GmbH
- KBS Industrieelektronik GmbH
- Liv Tec GmbH
- Siemens AG
- Unity AG
- Zebra Technologies Germany GmbH
The IGF project 20263 N of the Forschungsvereinigung Bundesvereinigung Logistik e.V. - BVL, Schlachte 31, 28195 Bremen, was funded by the AiF within the programme for the promotion of joint industrial research (IGF) of the Federal Ministry of Economics and Energy on the basis of a resolution of the German Bundestag.
![[Translate to en:] Finger tippt an digitalen Zähler zur Inhaltsmenge einer Box](/fileadmin/w00cbp/fml/Forschung/Projekte/Abgeschlossene_Projekte_2021/Pick-by-Tag/Pick_by_Light_Quelle_KBS.jpg)