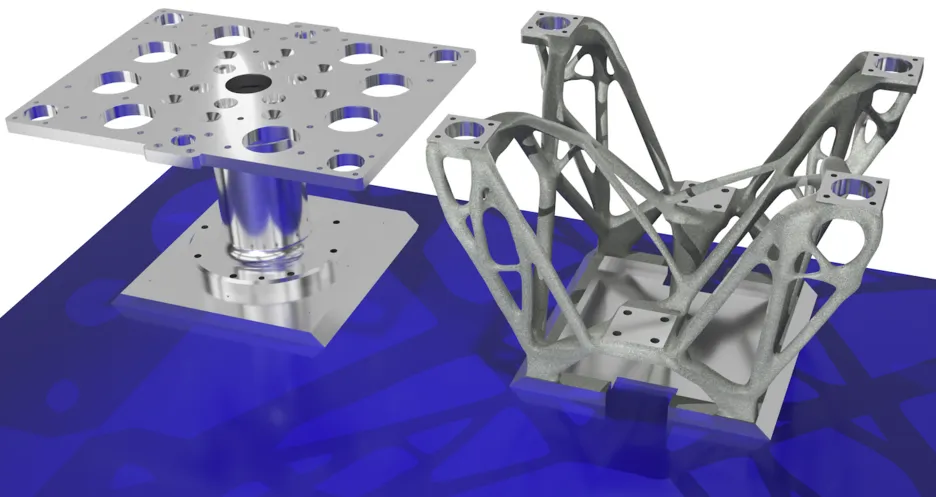
Problem
Additive manufacturing comprises a large number of very different technologies with specific advantages and disadvantages. Powder bed fusion of metals using a laser beam (PBFLB/M for short) dominates the processing of metallic materials. This enables high levels of detail to be achieved and the production of filigree and internal structures to be realized. Compared to PBF-LB/M, wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) is characterized by high deposition rates and an almost unlimited build volume. However, the achievable resolution is low, meaning that filigree structures cannot be produced. Internal geometries, such as cooling channels, are also not feasible.
Hybrid additive manufacturing offers the opportunity to overcome the above-mentioned restrictions of the processes and meet the requirements of the industry. It refers to a combination of different additive manufacturing processes, but also the combination of an additive with an established and cost-effective conventional manufacturing method. Both of these approaches can be suitable for combining economic and functional objectives in component design and production.
Goal
The aim of the KREATIVE research project is to develop a design methodology for the production of a component by combining different manufacturing processes. In addition to the manufacturability of the component, factors such as lower costs, improved functionality and increased resource efficiency are also considered. Modeling and design processes are used for the product development phase. The design of the components is supported by tools such as topology optimization.

